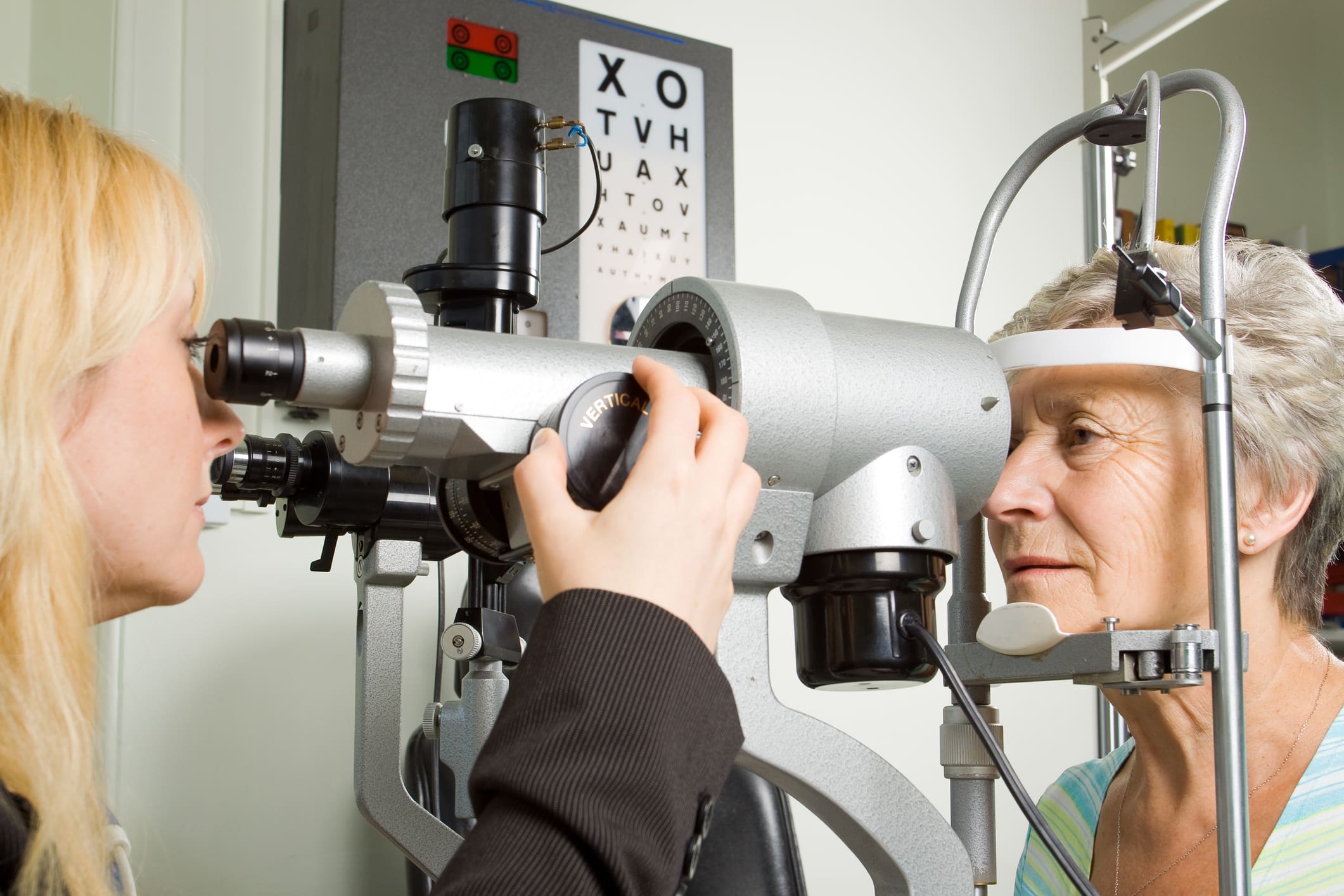
Laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis, commonly known as LASIK, stands as a beacon of modern medical…

Eye Trauma: A Surprising Catalyst for Cataract Development
The human eye, while robust in many ways, is vulnerable to various forms of injury and disease. One common eye condition that affects many individuals worldwide is cataracts. A cataract is the clouding of the natural lens of the eye, leading to vision impairment. While age is the most common catalyst for cataract development, less known is the role of eye trauma in triggering this condition.
Eye Trauma: An Unseen Trigger
Eye trauma, whether from a forceful blow, a sharp object, or intense heat or chemical exposure, can lead to various complications, including cataracts. The traumatic event may damage the lens fibers causing them to become opaque, a condition known as traumatic cataract. These cataracts can occur immediately after the injury or may develop several years later.
Understanding Traumatic Cataracts
Traumatic cataracts are unique in that their occurrence and progression are unpredictable. They can develop from minor eye injuries that might not be immediately apparent. Moreover, the type of trauma often influences the cataract’s appearance and location within the lens. For instance, blunt trauma can result in a star-shaped cataract, while penetrating injuries might lead to localized opacity where the object entered the lens.
The Science Behind Traumatic Cataracts
From a biological perspective, eye trauma leads to an increase in oxidative stress within the lens. This stress can damage the lens’s proteins, causing them to cluster together and form opaque areas, leading to cataract formation. Furthermore, trauma-induced inflammation can disrupt the eye’s natural healing process, exacerbating lens damage and cataract development.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing traumatic cataracts involves a thorough eye examination, often accompanied by the patient’s history of eye injury. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) and slit-lamp examination can provide a detailed view of the lens and help identify any opacities.
Treatment usually involves cataract surgery to replace the damaged lens with an artificial one. The timing of surgery depends on the cataract’s size, location, and impact on vision, as well as the presence of any other eye injuries.
Prevention: Safety First
Preventing traumatic cataracts primarily involves eye safety. This can include wearing protective eyewear during high-risk activities like sports or certain occupations, ensuring safe practices around chemicals and heat, and seeking immediate medical attention after an eye injury.
Eye Trauma and Cataracts: A Crucial Connection
Eye trauma serves as a critical catalyst for cataract development, an aspect that highlights the importance of eye safety in preventing vision impairment. Through understanding the mechanisms of traumatic cataracts, from their unpredictable onset to their biological underpinnings, individuals and medical professionals alike can better approach eye trauma management and cataract prevention.
Moreover, this knowledge promotes proactive eye care, allowing for early detection, intervention, and treatment of traumatic cataracts. This proactive approach, in turn, can make a significant difference in preserving vision and maintaining overall eye health.
Don’t compromise on your eye health and vision. Reach out to our team of professionals today, and let’s work together to safeguard your eyes against trauma and potential cataract development.